Section 3.1 Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration
|
In diving to a depth of 750 m, an elephant seal also moves 460 m due east of his starting point. What is the magnitude of the seal’s displacement?
|  | |
A baseball player hits a triple and ends up on third base. A baseball “diamond” is a square, each side of length 27.4 m, with home plate and the three bases on the four corners. What is the magnitude of his displacement?
|
A mountain-climbing expedition establishes two intermediate camps, labeled A and B in the drawing, above the base camp. What is the magnitude D of the displacement between camp A and camp B?
|  | |
The altitude of a hang glider is increasing at a rate of 6.80 m/s. At the same time, the shadow of the glider moves along the ground at a speed of 15.5 m/s when the sun is directly overhead. Find the magnitude of the glider’s velocity.
|
A jetliner is moving at a speed of 245 m/s. The vertical component of the plane’s velocity is 40.6 m/s. Determine the magnitude of the horizontal component of the plane’s velocity.
|  | |
In a football game a kicker attempts a field goal. The ball remains in contact with the kicker’s foot for 0.050 s, during which time it experiences an acceleration of 340 m/s2. The ball is launched at an angle of 51° above the ground. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the launch velocity.
|
A dolphin leaps out of the water at an angle of 35° above the horizontal. The horizontal component of the dolphin’s velocity is 7.7 m/s. Find the magnitude of the vertical component of the velocity.
|  | |
A skateboarder, starting from rest, rolls down a 12.0-m ramp. When she arrives at the bottom of the ramp her speed is 7.70 m/s. (a) Determine the magnitude of her acceleration, assumed to be constant. (b) If the ramp is inclined at 25.0° with respect to the ground, what is the component of her acceleration that is parallel to the ground?
|
In a mall, a shopper rides up an escalator between floors. At the top of the escalator, the shopper turns right and walks 9.00 m to a store. The magnitude of the shopper’s displacement from the bottom of the escalator is 16.0 m. The vertical distance between the floors is 6.00 m. At what angle is the escalator inclined above the horizontal?
|  | |
Interactive LearningWare 3.1 reviews the approach taken in problems such as this one. A bird watcher meanders through the woods, walking 0.50 km due east, 0.75 km due south, and 2.15 km in a direction 35.0° north of west. The time required for this trip is 2.50 h. Determine the magnitude and direction (relative to due west) of the bird watcher’s (a) displacement and (b) average velocity. Use kilometers and hours for distance and time, respectively.
Section 3.2 Equations of Kinematics in Two Dimensions, Section 3.3 Projectile Motion
A spacecraft is traveling with a velocity of v0x =
= 5480 m/s along the +x direction. Two engines are turned on for a time of 842 s. One engine gives the spacecraft an acceleration in the +x direction of ax
5480 m/s along the +x direction. Two engines are turned on for a time of 842 s. One engine gives the spacecraft an acceleration in the +x direction of ax =
= 1.20 m/s2, while the other gives it an acceleration in the +y direction of ay
1.20 m/s2, while the other gives it an acceleration in the +y direction of ay =
= 8.40 m/s2. At the end of the firing, find (a) vx and (b) vy.
8.40 m/s2. At the end of the firing, find (a) vx and (b) vy.
|
A tennis ball is struck such that it leaves the racket horizontally with a speed of 28.0 m/s. The ball hits the court at a horizontal distance of 19.6 m from the racket. What is the height of the tennis ball when it leaves the racket?
|  | |
A volleyball is spiked so that it has an initial velocity of 15 m/s directed downward at an angle of 55° below the horizontal. What is the horizontal component of the ball’s velocity when the opposing player fields the ball?
|
A golf ball rolls off a horizontal cliff with an initial speed of 11.4 m/s. The ball falls a vertical distance of 15.5 m into a lake below. (a) How much time does the ball spend in the air? (b) What is the speed v of the ball just before it strikes the water?
|  | |
A rock climber throws a small first aid kit to another climber who is higher up the mountain. The initial velocity of the kit is 11 m/s at an angle of 65° above the horizontal. At the instant when the kit is caught, it is traveling horizontally, so its vertical speed is zero. What is the vertical height between the two climbers?
|
A diver runs horizontally with a speed of 1.20 m/s off a platform that is 10.0 m above the water. What is his speed just before striking the water?
|  | |
Concept Simulation 3.2 reviews the concepts that are important in this problem. A golfer imparts a speed of 30.3 m/s to a ball, and it travels the maximum possible distance before landing on the green. The tee and the green are at the same elevation. (a) How much time does the ball spend in the air? (b) What is the longest “hole in one” that the golfer can make, if the ball does not roll when it hits the green?
|
Review Interactive LearningWare 3.2 in preparation for this problem. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon has a magnitude of 1.62 m/s. Examples 5, 6 and 7 deal with a placekicker kicking a football. Assume that the ball is kicked on the moon instead of on the earth. Find (a) the maximum height H and (b) the range that the ball would attain on the moon.
|  | |
Michael Jordan, formerly of the Chicago Bulls basketball team, has some fanatic fans. They claim that he is able to jump and remain in the air for two full seconds from launch to landing. Evaluate this claim by calculating the maximum height that such a jump would attain. For comparison, Jordan’s maximum jump height has been estimated at about one meter.
|
A fire hose ejects a stream of water at an angle of 35.0° above the horizontal. The water leaves the nozzle with a speed of 25.0 m/s. Assuming that the water behaves like a projectile, how far from a building should the fire hose be located to hit the highest possible fire?
|  | |
A car drives straight off the edge of a cliff that is 54 m high. The police at the scene of the accident note that the point of impact is 130 m from the base of the cliff. How fast was the car traveling when it went over the cliff?
|
Interactive LearningWare 3.2 provides a review of the concepts that are important in this problem.On a distant planet, golf is just as popular as it is on earth. A golfer tees off and drives the ball 3.5 times as far as he would have on earth, given the same initial velocities on both planets. The ball is launched at a speed of 45 m/s at an angle of 29° above the horizontal. When the ball lands, it is at the same level as the tee. On the distant planet, what is (a) the maximum height and (b) the range of the ball?
|  | |
The 1994 Winter Olympics included the aerials competition in skiing. In this event skiers speed down a ramp that slopes sharply upward at the end. The sharp upward slope launches them into the air, where they perform acrobatic maneuvers. In the women’s competition, the end of a typical launch ramp is directed 63° above the horizontal. With this launch angle, a skier attains a height of 13 m above the end of the ramp. What is the skier’s launch speed?
|
An eagle is flying horizontally at 6.0 m/s with a fish in its claws. It accidentally drops the fish. (a) How much time passes before the fish’s speed doubles? (b) How much additional time would be required for the fish’s speed to double again?
|  | |
A major-league pitcher can throw a baseball in excess of 41.0 m/s. If a ball is thrown horizontally at this speed, how much will it drop by the time it reaches a catcher who is 17.0 m away from the point of release?
|
A motorcycle daredevil is attempting to jump across as many buses as possible (see the drawing). The takeoff ramp makes an angle of 18.0° above the horizontal, and the landing ramp is identical to the takeoff ramp. The buses are parked side by side, and each bus is 2.74 m wide. The cyclist leaves the ramp with a speed of 33.5 m/s. What is the maximum number of buses over which the cyclist can jump?
|  | |
Suppose the water at the top of Niagara Falls has a horizontal speed of 2.7 m/s just before it cascades over the edge of the falls. At what vertical distance below the edge does the velocity vector of the water point downward at a 75° angle below the horizontal?
|
A hot-air balloon is rising straight up with a speed of 3.0 m/s. A ballast bag is released from rest relative to the balloon when it is 9.5 m above the ground. How much time elapses before the ballast bag hits the ground?
|  | |
A rocket is fired at a speed of 75.0 m/s from ground level, at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal. The rocket is fired toward an 11.0-m-high wall, which is located 27.0 m away. By how much does the rocket clear the top of the wall?
|
A horizontal rifle is fired at a bull’s-eye. The muzzle speed of the bullet is 670 m/s. The barrel is pointed directly at the center of the bull’s-eye, but the bullet strikes the target 0.025 m below the center. What is the horizontal distance between the end of the rifle and the bull’s-eye?
|  | |
An airplane with a speed of 97.5 m/s is climbing upward at an angle of 50.0° with respect to the horizontal. When the plane’s altitude is 732 m, the pilot releases a package. (a) Calculate the distance along the ground, measured from a point directly beneath the point of release, to where the package hits the earth. (b) Relative to the ground, determine the angle of the velocity vector of the package just before impact.
|
An Olympic long jumper leaves the ground at an angle of 23° and travels through the air for a horizontal distance of 8.7 m before landing. What is the takeoff speed of the jumper?
|  | |
Review Conceptual Example 4 and Concept Simulation 3.1 before beginning this problem. You are traveling in a convertible with the top down. The car is moving at a constant velocity of 25 m/s, due east along flat ground. You throw a tomato straight upward at a speed of 11 m/s. How far has the car moved when you get a chance to catch the tomato?
|
As an aid in working this problem, consult Interactive Solution 3.35 . A soccer player kicks the ball toward a goal that is 16.8 m in front of him. The ball leaves his foot at a speed of 16.0 m/s and an angle of 28.0° above the ground. Find the speed of the ball when the goalie catches it in front of the net.
|  | |
In the javelin throw at a track-and-field event, the javelin is launched at a speed of 29 m/s at an angle of 36° above the horizontal. As the javelin travels upward, its velocity points above the horizontal at an angle that decreases as time passes. How much time is required for the angle to be reduced from 36° at launch to 18°?
|
Stones are thrown horizontally with the same velocity from the tops of two different buildings. One stone lands twice as far from the base of the building from which it was thrown as does the other stone. Find the ratio of the height of the taller building to the height of the shorter building.
|  | |
|
Before beginning this problem, review Interactive Solution 3.39 . After leaving the end of a ski ramp, a ski jumper lands downhill at a point that is displaced 51.0 m horizontally from the end of the ramp. His velocity, just before landing, is 23.0 m/ points in a direction 43.0°w the horizontal. Neglecting air resistance and any lift he experiences while airborne, find his initial velocity (magnitude and direction) when he left the end of the ramp. Express the direction as an angle relative to the horizontal.
|  | |
The lob in tennis is an effective tactic when your opponent is near the net. It consists of lofting the ball over his head, forcing him to move quickly away from the net (see the drawing). Suppose that you loft the ball with an initial speed of 15.0 m/s at an angle of 50.0° the horizontal. At this instant your opponent is 10.0 m away from the ball. He begins moving away from you 0.30 s later, hoping to reach the ball and hit it back at the moment that it is 2.10 m above its launch point. With what minimum average speed must he move? (Ignore the fact that he can stretch, so that his racket can reach the ball before he does.)
A placekicker is about to kick a field goal. The ball is 26.9 m from the goalpost. The ball is kicked with an initial velocity of 19.8 m/s at an angle 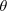 above the ground. Between what two angles,
above the ground. Between what two angles,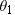 and
and 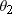 , will the ball clear the 2.74-m-high crossbar?
, will the ball clear the 2.74-m-high crossbar?
|
From the top of a tall building, a gun is fired. The bullet leaves the gun at a speed of 340 m/s, parallel to the ground. As the drawing shows, the bullet puts a hole in a window of another building and hits the wall that faces the window. Using the data in the drawing, determine the distances D and H, which locate the point where the gun was fired. Assume that the bullet does not slow down as it passes through the window.
|  | |
A baseball is hit into the air at an initial speed of 36.6 m/s and an angle of 50.0° above the horizontal. At the same time, the center fielder starts running away from the batter and catches the ball 0.914 m above the level at which it was hit. If the center fielder is initially 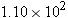 m from home plate, what must be his average speed?
m from home plate, what must be his average speed?
|
Two cannons are mounted as shown in the drawing and rigged to fire simultaneously. They are used in a circus act in which two clowns serve as human cannonballs. The clowns are fired toward each other and collide at a height of 1.00 m above the muzzles of the cannons. Clown A is launched at a 75.0° angle, with a speed of 9.00 m/s. The horizontal separation between the clowns as they leave the cannons is 6.00 m. Find the launch speed v0B and the launch angle 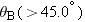 for clown B. for clown B.
|  | |
A small can is hanging from the ceiling. A rifle is aimed directly at the can, as the figure illustrates. At the instant the gun is fired, the can is released. Ignore air resistance and show that the bullet will always strike the can, regardless of the initial speed of the bullet. Assume that the bullet strikes the can before the can reaches the ground.
Section 3.4 Relative Velocity
|
Two passenger trains are passing each other on adjacent tracks. Train A is moving east with a speed of 13 m/s, and train B is traveling west with a speed of 28 m/s. (a) What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of train A as seen by the passengers in train B? (b) What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of train B as seen by the passengers in train A?
|  | |
Two cars, A and B, are traveling in the same direction, although car A is 186 m behind car B. The speed of A is 24.4 m/s, and the speed of B is 18.6 m/s. How much time does it take for A to catch B?
|
At some airports there are speed ramps to help passengers get from one place to another. A speed ramp is a moving conveyor belt that you can either stand or walk on. Suppose a speed ramp has a length of 105 m and is moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s relative to the ground. In addition, suppose you can cover this distance in 75 s when walking on the ground. If you walk at the same rate with respect to the speed ramp that you walk with respect to the ground, how long does it take for you to travel the 105 m using the speed ramp?
|  | |
The escalator that leads down into a subway station has a length of 30.0 m and a speed of 1.8 m/s relative to the ground. A student is coming out of the station by running in the wrong direction on this escalator. The local record time for this trick is 11 s. Relative to the escalator, what speed must the student exceed in order to beat the record?
|
A swimmer, capable of swimming at a speed of 1.4 m/s in still water (i.e., the swimmer can swim with a speed of 1.4 m/s relative to the water), starts to swim directly across a 2.8-km-wide river. However, the current is 0.91 m/s, and it carries the swimmer downstream. (a) How long does it take the swimmer to cross the river? (b) How far downstream will the swimmer be upon reaching the other side of the river?
|  | |
On a pleasure cruise a boat is traveling relative to the water at a speed of 5.0 m/s due south. Relative to the boat, a passenger walks toward the back of the boat at a speed of 1.5 m/s. (a) What is the magnitude and direction of the passenger’s velocity relative to the water? (b) How long does it take for the passenger to walk a distance of 27 m on the boat? (c) How long does it take for the passenger to cover a distance of 27 m on the water?
|
You are in a hot-air balloon that, relative to the ground, has a velocity of 6.0 m/s in a direction due east. You see a hawk moving directly away from the balloon in a direction due north. The speed of the hawk relative to you is 2.0 m/s. What are the magnitude and direction of the hawk’s velocity relative to the ground? Express the directional angle relative to due east.
|  | |
The captain of a plane wishes to proceed due west. The cruising speed of the plane is 245 m/s relative to the air. A weather report indicates that a 38.0-m/s wind is blowing from the south to the north. In what direction, measured with respect to due west, should the pilot head the plane relative to the air?
|
As an aid in working this problem, consult Interactive Solution 3.55 . A ferryboat is traveling in a direction 38.0° north of east with a speed of 5.50 m/s relative to the water. A passenger is walking with a velocity of 2.50 m/s due east relative to the boat. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the passenger with respect to the water? Determine the directional angle relative to due east.
|  | |
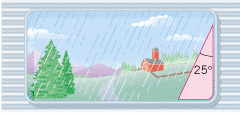
A person looking out the window of a stationary train notices that raindrops are falling vertically down at a speed of 5.0 m/s relative to the ground. When the train moves at a constant velocity, the raindrops make an angle of 25° when they move past the window, as the drawing shows. How fast is the train moving?
|
A small aircraft is headed due south with a speed of 57.8 m/s with respect to still air. Then, for 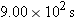 a wind blows the plane so that it moves in a direction 45.0° west of south, even though the plane continues to point due south. The plane travels 81.0 km with respect to the ground in this time. Determine the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the wind with respect to the ground. Determine the directional angle relative to due south. a wind blows the plane so that it moves in a direction 45.0° west of south, even though the plane continues to point due south. The plane travels 81.0 km with respect to the ground in this time. Determine the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the wind with respect to the ground. Determine the directional angle relative to due south.
|  | |
Two boats are heading away from shore. Boat 1 heads due north at a speed of 3.00 m/s relative to the shore. Relative to Boat 1, Boat 2 is moving 30.0° north of east at a speed of 1.60 m/s. A passenger on Boat 2 walks due east across the deck at a speed of 1.20 m/s relative to Boat 2. What is the speed of the passenger relative to the shore?
|
A Coast Guard ship is traveling at a constant velocity of 4.20 m/s, due east, relative to the water. On his radar screen the navigator detects an object that is moving at a constant velocity. The object is located at a distance of 2310 m with respect to the ship, in a direction 32.0° south of east. Six minutes later, he notes that the object’s position relative to the ship has changed to 1120 m, 57.0° south of west. What are the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the object relative to the water? Express the direction as an angle with respect to due west.
|  | |
 |
| Copyright © 2000-2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. or related companies. All rights reserved. |
![]() =
=![]() 5480 m/s along the +x direction. Two engines are turned on for a time of 842 s. One engine gives the spacecraft an acceleration in the +x direction of ax
5480 m/s along the +x direction. Two engines are turned on for a time of 842 s. One engine gives the spacecraft an acceleration in the +x direction of ax![]() =
=![]() 1.20 m/s2, while the other gives it an acceleration in the +y direction of ay
1.20 m/s2, while the other gives it an acceleration in the +y direction of ay![]() =
=![]() 8.40 m/s2. At the end of the firing, find (a) vx and (b) vy.
8.40 m/s2. At the end of the firing, find (a) vx and (b) vy.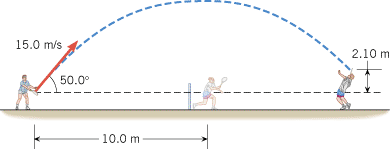
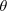 above the ground. Between what two angles,
above the ground. Between what two angles,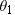 and
and 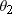 , will the ball clear the 2.74-m-high crossbar?
, will the ball clear the 2.74-m-high crossbar?
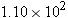 m from home plate, what must be his average speed?
m from home plate, what must be his average speed?