Resistance; Ohm's Law
Topics and Files
E&M Topics
- Ohm's Law
- Series and parallel circuits
DataStudio Files
- 67 Ohm's Law.ds
- 69 Resistors.ds
Equipment List
Introduction
This lab has two parts. The purpose of Experiment 1 is to confirm the relationship of current, voltage, and resistance in an electric circuit. You will also explore what happens to the resistance of a light bulb's filament as it changes temperature. Use the DataStudio software to measure the current through resistors and the filament of a light bulb as the voltage across the resistors and the filament of the light bulb is changed. The purpose of Experiment 2 is to confirm that when resistors are added in series to a circuit, they have a total resistance that equals the sum of their individual resistances, and that when resistors are added in parallel to a circuit, they have a total resistance that is less than the individual resistances. Use a voltage sensor, a current sensor, and the DataStudio software to measure the voltage across parts of the series and parallel circuits, and a current sensor to measure the current through the circuits.Background
Ohm discovered that when the voltage (potential difference) across a resistor changes, the current through the resistor changes. He expressed this as( 1 )
I =
| V |
| R |
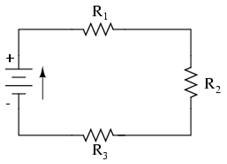
Figure 1
 |
| V |
| I |
 |
( 2 )
V = V1 + V2 + V3 = IR1 + IR2 + IR3 = I(R1 + R2 + R3) = IRTotal
RTotal
is the sum of the individual resistances.
Components in a series circuit share the same current.
( 3 )
ITotal = I1 = I2 =  In
In
 In
In ( 4 )
RTotal = R1 + R2 +  Rn
Rn
 Rn
Rn ( 5 )
VTotal = V1 + V2 +  Vn
Vn
 Vn
Vn 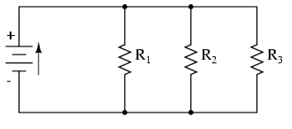
Figure 2
( 6 )
I = I1 + I2 + I3 =
+
+
= V
+
+
= V
| V |
| R1 |
| V |
| R2 |
| V |
| R3 |
 |
| 1 |
| R1 |
| 1 |
| R2 |
| 1 |
| R3 |
 |
 |
| 1 |
| REquivalent |
 |
REquivalent
from the other individual resistances as follows.
( 7 )
REquivalent =
| 1 | ||||||
 |
( 8 )
VTotal = V1 = V2 =  Vn
Vn
 Vn
Vn ( 9 )
RTotal = 1/(1/R1 + 1/R2 +  1/Rn)
1/Rn)
 1/Rn)
1/Rn) ( 10 )
Itotal = I1 + I2 +  In
In
 In
In 

