Earth's Magnetic Field; Magnetic Field of Permanent Magnet
Topics and Files
E&M Topics
- Earth's magnetic field; dip angle
- Magnetic field strength vs distance
Capstone Files
- 77 Earth Mag Field.cap
- 78 Permanent Magnet.cap
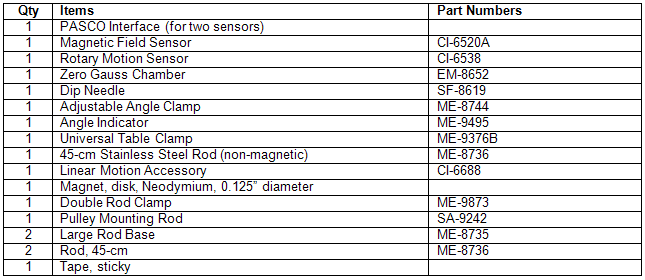
Equipment List
Introduction
This lab has two parts. The purpose of Experiment 1 is to measure the magnitude and direction of the Earth's magnetic field. Use a magnetic field sensor mounted on a rotary motion sensor. Rotate the magnetic field sensor on the rotary motion sensor to measure the directional variation in the Earth's field. Use Capstone to measure and display the magnetic field strength versus direction. The purpose the Experiment 2 is to measure the magnitude field strength of a small neodymium magnet as the distance from the magnet increases. Use a magnetic field sensor and a rotary motion sensor. Use Capstone to measure and display the magnetic field strength versus distance.Background
The magnitude of the Earth's magnetic field varies over the surface of the Earth. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field points north (toward the magnetic south). Thus, the north end of a compass needle is attracted to the south end of the Earth's magnetic field. Therefore, the pole that is referred to as "north" is actually a south magnetic pole. The total magnetic field points at an angle from the horizontal. This angle (θ) is called the dip angle. An example for the northern hemisphere is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
( 1 )
cos θ =
| BHorizontal |
| BTotal |

Figure 2