Appendix K: Using a Mutimeter
A multimeter can be used as an ammeter to measure current, as a voltmeter to measure potential difference, and as an ohmmeter to measure resistance. It can measure both AC and DC currents and voltages. To avoid damaging the multimeter and other components in a circuit, it is critical to use the correct setting for the kind of measurement you will be making.
Figure 1: A typical multimeter
Using the multimeter as a voltmeter
-
1Set the dial to the symbol with the line and dots next to V) to measure DC voltage (see Fig. 2 below).
-
2Plug the red probe lead into the socket labelled VΩHz.
-
3Plug the black lead into the socket labelled COM.
-
4To measure the potential difference across a resistor, touch the red and black leads on opposite sides of the resistor. See the circuit diagram in Fig 2.
-
5Record the absolute value shown on the multimeter's screen.
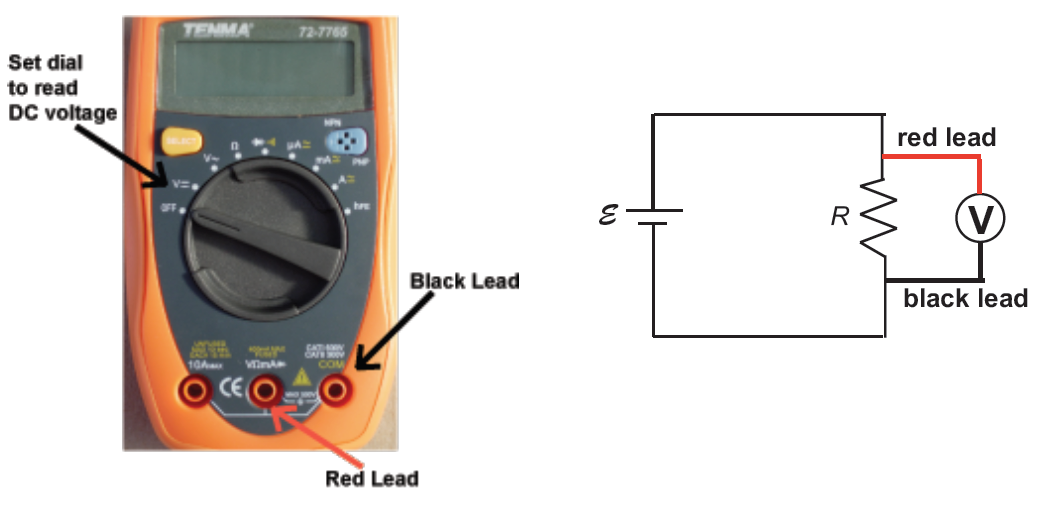
Figure 2: Using a multimeter as a voltmeter
Using the multimeter as an ammeter
-
1Set the dial to mA to measure current (see Fig. 3 below).
-
2Plug the red probe lead into the socket labelled VΩHz.
-
3Plug the black lead into the socket labelled COM.
-
4To measure the current through a resistor, connect the ammeter in series with the resistor. See the circuit diagram in Fig. 3. In general, you will have to disconnect the circuit to clip the red and black leads into the circuit.
-
5Record the value shown on the multimeter's screen.
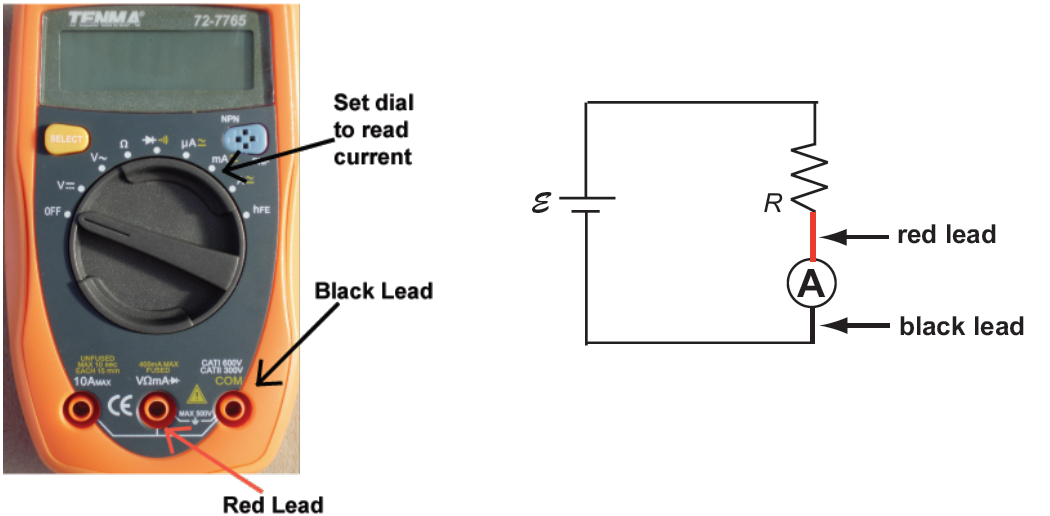
Figure 3: Using a multimeter as an ammeter
