Lab 1 - Reaction Stoichiometry
Purpose
To determine the stoichiometry of acid-base reactions by measuring temperature changes which accompany them.Goals
-
1To learn to use the MicroLab Interface.
-
2To practice generating reaction tables.
-
3To determine the limiting reagent in a reaction through a measured quantity.
Introduction
In this lab, you will be investigating reaction stoichiometry by doing a series of mixing experiments using acids and bases in different amounts. By following temperature changes upon mixing, you will be able to relate the amount of heat given off in the reaction to the moles of acid and base that react. The first set of experiments uses the neutralization of HCl with sodium hydroxide:( 1 )
WaTeX parsing error.
( 2 )
H3PO4(aq) + 3 NaOH(aq) → Na3PO4(aq) + 3 H2O
( 3 )
2 Al + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2
( 4 )
moles HCl needed = 65 g Al ×
×
= 7.28 mol HCl
| 1 |
| 27.0 |
| 6 mol HCl |
| 2 |
( 5 )
grams AlCl3 produced = 65.5 g Al ×
×
×
= 323 g AlCl3
| 1 |
| 27.0 |
| 2 |
| 2 |
| 133 g AlCl3 |
| 1 |
( 6 )
grams AlCl3 produced = 6.00 mol HCl ×
×
= 266 g AlCl3
| 2 |
| 6 |
| 133 g AlCl3 |
| 1 |
( 7 )
Percent yield =
× 100%
| actual yield (g or mol) |
| theoretical yield (g or mol) |
( 8 )
| 255 |
| 266 |
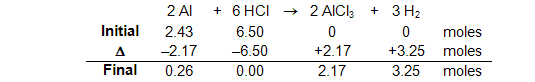 In this table:
In this table:
- Initial: The starting amounts expressed in moles or mmoles.
- Δ (or change): The amount of change that occurs in the reaction expressed in moles or mmoles. Note that as the reaction proceeds, the reactant side decreases (hence the - sign) and the product side increases (the + sign). IT IS ON THIS LINE WHERE THE REACTION STOICHIOMETRY AND LIMITING REACTANT ARE ACCOUNTED FOR. This has been indicated in the table by the use of all of the HCl and the use of the stoichiometric amount of Al along with the stoichiometric equivalents of the products based on the HCl being the limiting reactant.
- Final: The amount of material remaining after the reaction is complete or equilibrium is established. It is the algebraic sum of INITIAL + Δ.
( 9 )
20 mL NaOH solution ×
= 26 mmol NaOH
| 1.3 mmol NaOH |
| 1.0 mL solution |
Equipment
-
4150 mL beakers
-
350 mL graduated cylinder
-
1MicroLab Interface
-
1MicroLab Thermistor Instruction Sheet
-
1thermistor
-
1deionized water squirt bottle
-
1ring stand
-
1clamp
Reagents
-
60 mL1.5 M HCl (aq)
-
45 mL1.0 M H3PO4(aq)
-
150 mL1.5 M NaOH (aq)
Safety
You will be working with hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq); phosphoric acid, H3PO4 (aq); and NaOH (aq). These chemicals are corrosive. If you spill one of them on a surface, wipe it up with paper towels and rinse with water, being careful not to touch the liquid. If you spill some on yourself, immediately rinse the area with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. If any of these chemicals gets in your eyes, flush your eyes with water at the eyewash station for at least 15 minutes and have someone notify the TA. Students will have access to gloves due to the use of concentrated acid and base solutions during the lab period.Waste Disposal
The solutions used in this experiment can be disposed of down the sink drain followed by flushing with plenty of water.Prior to Class
Please read the following section of Lab Safety and Practices: Please read the following section in Lab Equipment: Please review the following video: Please complete WebAssign prelab assignment. Check your WebAssign Account for due dates. Students who do not complete the WebAssign prelab are required to bring and hand in the prelab worksheet.Lab Procedure
Please print the worksheet for this lab. You will need this sheet to record your data and write out calculations.1
Open the MicroLab program.
2
Calibrate the thermistor as described in the MicroLab instructions provided in the lab.
3
After the calibration is complete, set the MicroLab collection increment to 2 seconds using the instructions provided.
4
In separate appropriately labeled 150 mL beakers, obtain the total amount of acid and base solutions you will need for each set of experiments: 60 mL HCl, 45 mL H3PO4 and 150 mL NaOH. Record their concentrations in Data Table A.
Table A: Stock solution concentrations of HCl, H3PO4 and NaOH
5
Label a graduated cylinder for acid, another for base and a third for deionized water. Use them consistently for the liquid designated. For each experiment, add the NaOH solution and the deionized water together in a 150 mL beaker, and immerse the thermistor part way into the liquid being careful not to touch the thermistor to the bottom or sides of the vessel.
6
Add the appropriate amount of NaOH solution (20 mL) and deionized water (20 mL) for the first run to a 150 mL beaker. Do not, at this point, handle the beaker since we only want to measure the heat evolved from the reaction. Use a clamp to hold the thermistor in place in the beaker to prevent it from touching the bottom and prevent the beaker from tipping over.
7
Measure the initial temperature of the base (NaOH solution, diluted with water). You may need to wait ~2 minutes to be sure the temperature has stabilized. Record its temperature to the nearest 0.01°C in Data Table B.
8
Add the appropriate amount of acid solution and swirl the beaker gently. If you swirl too vigorously, you may spill the acid and base on your hand. Do not stir with the thermistor as it can easily break. After the temperature stops changing (~30 sec), stop the temperature collection program. Record this final temperature to the nearest 0.01°C in Data Table B. Note: after stabilizing, the temperature may slowly, over the course of many minutes, decrease toward room temperature. Record the first stable temperature as your final temperature.
Question 1: Show your calculation for the mmol of base and the mmol of acid in mixing experiment 1. Use the same technique for experiments 2-6.
Table B: Temperature data for combinations of NaOH and HCl
Table C: Temperature data for combinations of NaOH and H3PO4
9
Dispose of the solution from the first run and rinse the reaction beaker and thermistor thoroughly with deionized water from your squirt bottle.
10
Obtain temperature change data for the other 5 mixing experiments by repeating steps 6 - 9. Remember to record both your initial and final temperatures for each experiment in Data Tables B and C.
Question 2: Construct a reaction table in millimoles for experiment 1.
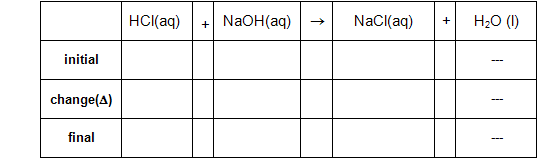

Queston 3: What is the limiting reagent in mixing experiment 1?
Question 4: Which experiments from 1-3 have the same change in temperature?
Question 5: For the experiments from 1-3 with the same temperature change, what other parameters are the same? Select all that apply.
|
|
11
Close the MicroLab software. Rinse all of your glassware with water, dry it and return it to the set-up area where you found it.
12
Before leaving, enter your results in the WebAssign InLab assignment. If all results are scored as correct, log out. If not all results are correct, try to find the error or consult with your teaching assistant. When all results are correct, note them and log out of WebAssign. The InLab assignment must be completed by the end of the lab period. If additional time is required, please consult with your teaching assistant.