|
Writing Chemical Equations
Writing correct chemical equations requires that you know how to predict products of reactions. Even with limited experience, one can use a few guidelines to accomplish this. Seven frequently used elements naturally occurring as diatomic molecules: H2. O2, N2, Cl2, Br2, I2. This is how they should always be written in a chemical equation. Ionic species are in aqueous solution, (aq); States of matter should be included by (s),(l),(g) after the chemical symbol. GENERAL CLASSIFICATIONS OF REACTIONS
SOLUBILITY RULES: SOLUBLE: All Nitrates, Acetates, Ammonium and Group I salts All Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides, except Silver, Lead & Mercury(I) All Fluorides except Group II, Lead(II), and Iron(III) All Sulfates except Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Mercury, Lead(II), and Ag. INSOLUBLE: All Carbonates & Phosphates except Group I and Ammonium(NH4+) All Hydroxides except Group I, Sr, Ba All Sulfides except Group I,II, and NH4+ All Oxides except Group I INSOLUBLE means a precipitate forms when equal volumes of 0.10 M solutions or greater are mixed 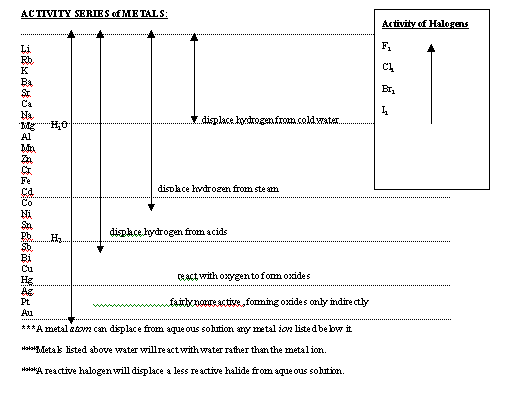
Back to Chemistry Reference Data Prepared with the support and help of the North Carolina Department of Public Instruction. |
