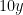By the additive property of the derivative, to find the derivative of the left-hand side of
2x2y + 5y2x = −2.
we can find the derivative of each term separately.
The first term of the left side of the equation is
2x2y.
Use the product rule to find the derivative of this term with respect to
x.
| [2x2y] | = | 2x2 + y [2x2] |
| |
| = | 2x2 + y

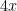
|
The second term of the left side of the equation is
5y2x.
Use the product rule again to find the derivative of this term with respect to
x.
| [5y2x] | = | 5y2 [x] + x [5y2] |
| |
| = | 5y2(1) + x

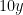
|
Therefore, by the additive property of the derivative, the derivative of the left side of the equation is as follows.
[
2x2y] +
[
5y2x] =
2x2 +
y(
4x) +
5y2(1) +
x